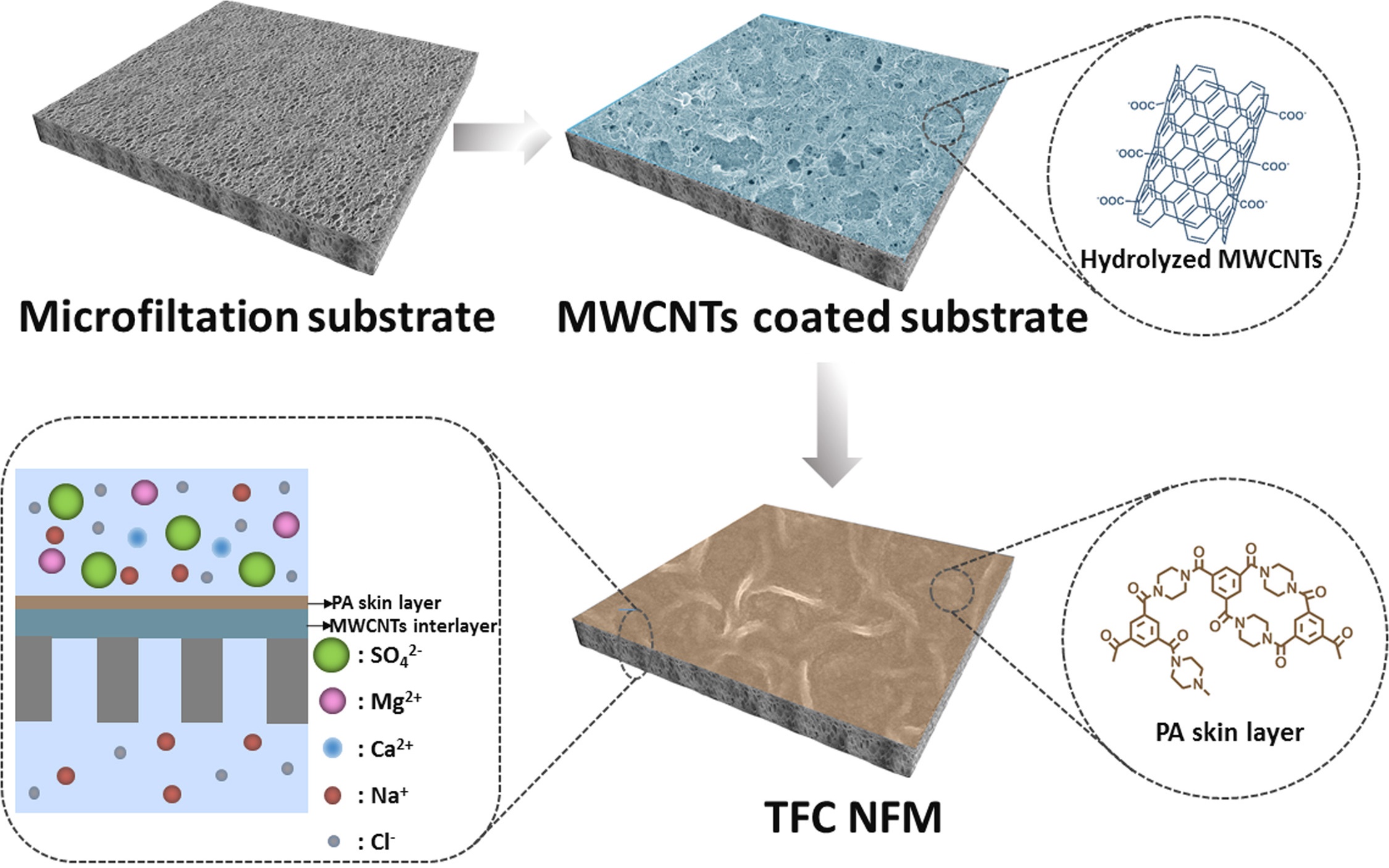
Interfacial polymerization and thin layer composite nanofiltration membrane
Nanofiltration technology has the characteristics of low energy consumption and high rejection. The importance of nanofiltration technology in seawater desalination, sewage treatment, food engineering and pharmaceutical industry has become increasingly prominent. The thin layer composite nanofiltration membrane with excellent performance is the core of nanofiltration technology. In this study, the surface interface control of thin layer composite nanofiltration membrane is the main research object. On the one hand, the traditional method of interface polymerization is improved. By introducing the intermediate layer to regulate the interface polymerization process, the nanofiltration structure is optimized and the high throughput nanofiltration membrane is prepared. On the other hand, the new nanofiltration membrane preparation technology is actively explored. By using the bionic co deposition and self standard effect of mussels, special types of nanofiltration membranes, such as organic inorganic compound, self cleaning surface and narrow pore size distribution, are prepared. Related literature are as follows:
1. Yan Lv, Chao Zhang and Zhi-Kang Xu, Photocatalytic Nanofiltration Membranes with Self-Cleaning Property for Wastewater Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27, 1700251;
2. Yong Du, Chao Zhang and Zhi-Kang Xu, Ultrathin Alginate Coatings as Selective Layers for Nanofiltration Membranes with High Performance. ChemSusChem, 2017, 10, 2788 – 2795;
3. Yan Lv, Hao-Cheng Yang and Zhi-Kang Xu,"Novel Nanofiltration Membrane with Ultrathin Zirconia Film as Selective Layer", J. Membr. Sci., 2016, 500, 265-271;
4. Xi Zhang, Peng-Fei Ren and Zhi-Kang Xu, "Co-deposition of Tannic Acid and Diethlyenetriamine for Surface Hydrophilization of Hydrophobic Polymer Membranes", Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 360, 291-297.
.png)