Congratulations to Shang-Jin Yang and Yan Lv for their publication on langmuir
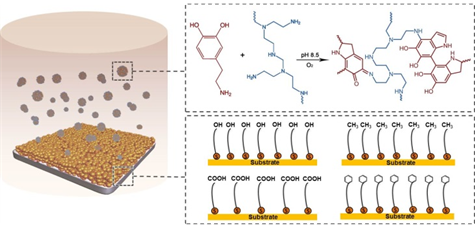
Polydopamine-based chemistry has been employed for various surface modifications attributed to the advantages of universality, versatility and simplicity. Co-deposition of polydopamine (PDA) with polyethyleneimine (PEI) has then been proposed to realize one-step fabrication of functional coatings with improved morphology uniformity, surface hydrophilicity and chemical stability. Herein, we report the co-deposition kinetics related to the solution composition with different dopamine/PEI ratios and PEI molecular weights, and the substrate surface with varying chemistry and wettability. The addition of PEI into dopamine solution suppresses the precipitation of PDA aggregates, resulting in an expanded time window of steady co-deposition compared with that of PDA deposition. Low-molecular-weight PEI at low concentration accelerates the co-deposition process while high-molecular-weight PEI and high concentration of either PEI or dopamine/PEI are detrimental to the co-deposition efficiency. It is revealed that deviations in co-deposition rate and amount for substrates bearing various functional groups of alkyl, phenyl, hydroxyl and carboxyl, which are quite different from the PDA deposition. The initial adsorption rates further reflect the change of interactions between the aggregates and these substrates by the introduced PEI, which follows the sequence of carboxyl > hydroxyl > alkyl > phenyl. These results provide deep insights into the PDA/PEI co-deposition process on various substrates.
DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02454
.png)